Writing Problem Statements
Project Life Cycle
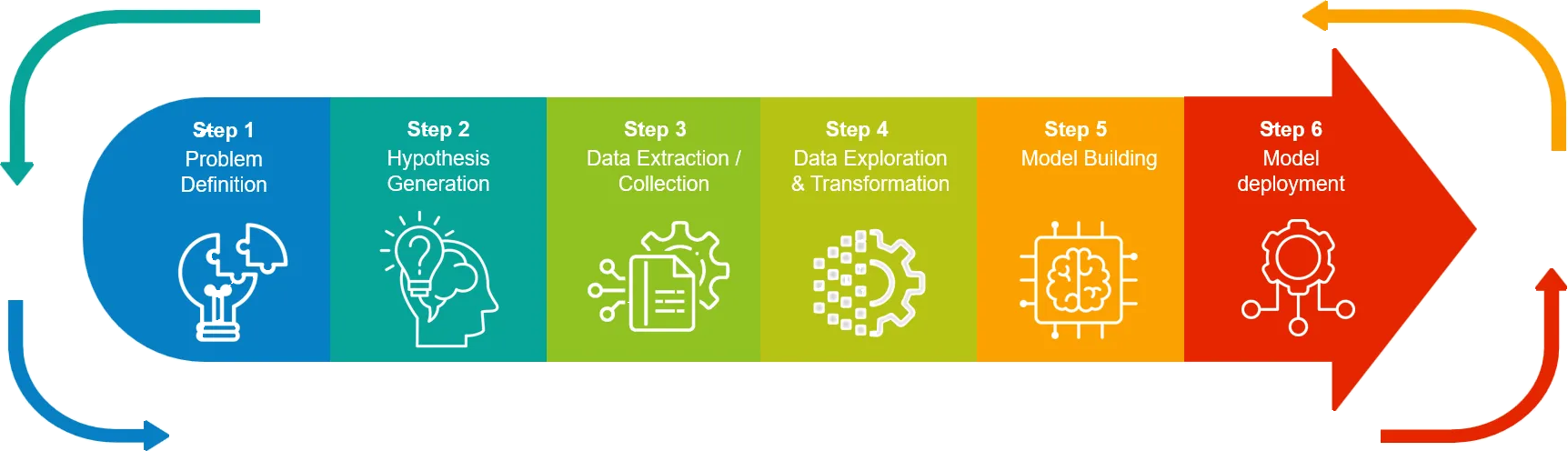
Image source: levelup.gitconnected.com
Problem Definition
Trouble - what does the project aim to solve?
Owner - who owns the problem? (business, stakeholders)
Success - what are the success criteria?
Constraints - logistical, budgetary, time…?
Actors - stakeholders and their interests
References - how have similar problems been solved in the past?
Example: University Enrollment
Costs of running a university are increasing, but the Board of Regents will not authorize tuition increases; as a result, UNL needs to recruit more students in order to continue to function as a state flagship university.
Trouble?
Owner?
Success criteria?
Constraints?
Actors?
References?
Writing the Problem Statement
Business problem -> general statement
Temporally focused
Incorporate constraints
Written to engage actors
Has to work within owner’s constraints
Example: University Enrollment
UNL needs to increase enrollment by 1% per year to offset cost increases due to inflation and reduce the need for tuition increases which would further strain Nebraskans’ budgets.
Break into Smaller Problems
Decomposition:
What factors contribute to enrollment gains/losses?Partition the space: mutually exclusive sub-problems
Recruitment, Retention, Registration
Convert Small Problems into Data Problems
What data do we have?
What data do we need?
Is it feasible to do the analysis with the resources available?
How complex is the analysis?
Activity
Pick a problem statement
Refine the problem statement
Swap with a classmate who selected a different statement
Peer review the refined problem statements
Share with the class
Problem statement topics
A. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is concerned that a concrete barrier will be picked up in a tornado and blown into a reactor building. Is this an issue that is sufficiently probable to address via changes to plant design?
B. Firearms and Toolmark (FATM) Examiners claim that subjective examination has an error rate of 2%, but the studies establishing this rate are unreliable. Do FATM examiners use methods which are sufficiently reliable to be presented in court?
C. One brand of vaccine requires one shot and has an 80% efficacy rate, while another brand requires two shots and has a 95% efficacy rate. Public Health officials want to know which shot has a better chance of stopping a global pandemic.